Use the CASE statement to define a multi-way conditional branch based on a comparison between a variable and one or more constants. When a match is found between a variable and a constant specified by a WHEN keyword, execution begins at the indicated WHEN and continues until the next WHEN, or until the end of the CASE structure.
An OTHERWISE statement is optional. You can use OTHERWISE to specify actions to be performed when none of the specified constants match. If OTHERWISE is not used and if none of the specified constants match, no action is taken and execution is resumed at the first statement following the ENDCASE statement.
Syntax
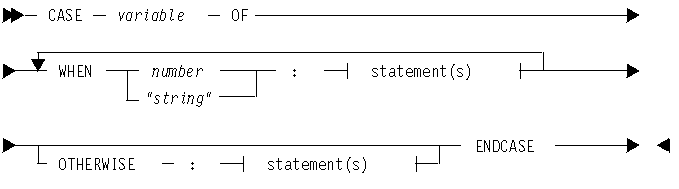
Examples
CASE count OF WHEN 1 : CALL Script_1; WHEN 2 : CALL Script_2; OTHERWISE : CALL Default_script; ENDCASE CASE screen_name OF WHEN "Main_menu" : . . . WHEN "Directory" : . . . ENDCASE
Procedure
To use the 3270 Script window’s Statements menu to define a CASE statement, follow this procedure:
- From the Welcome window, click on Applications —> 3270 Servers
- Selecting the CASE statement : Click Statements
—> Case.
The system displays the Case Definition window.
- Specifying the variable : Type the name of the variable that is to be tested in the Case field, or click Case to display the Term Definition window to select the variable.
- Adding WHEN keywords : Click Add once
for each test you want to perform in the CASE statement.
A Value field appears in the window each time you click Add.
- Type a value in each Value field that you want to compare to the Case variable, or click Value to display the Term Definition window to select the value.
- Deleting a value field : To delete a Value field, clear the field value (backspace) and click Delete.
- Adding the statement to the script : Click OK.
The CASE statement is added to the script.
- Defining WHEN statements : To define the statements to
be executed at each WHEN condition, position the cursor anywhere on
the line that contains the WHEN keyword, then click Statements to
define the required statements. Refer to the statement descriptions
for instructions. Note: The semicolon (;) following the WHEN keyword is automatically included when you define the CASE statement. Statements may immediately precede the semicolon, or may follow the semicolon. If no statements follow the WHEN keyword, the semicolon ensures legal syntax.
The statements are added to the script following the WHEN keywords.
- Defining OTHERWISE statements : To define statements to
be executed when none of the WHEN conditions are true, position the
cursor anywhere on the line that contains the OTHERWISE keyword, then
click Statements to define the required
statements. Refer to the statement descriptions for instructions.
The statements are added to the script following the OTHERWISE keyword.