When your voice applications are deployed, users simply
dial the telephone number that you provide and are connected to the
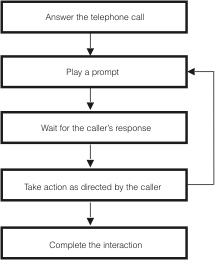
corresponding voice application. The figure below shows a flow chart
of a typical call.
|
- A user dials the telephone number you provide. WebSphere Voice
Response answers the call and executes the application referenced
by the dialed phone number.
- WebSphere Voice Server, or another MRCP-V1.0-compliant
speech product plays a greeting to the caller and prompts the
caller to indicate what information he or she wants.
- The application can use prerecorded greetings and prompts, or
the application can have the greeting or prompt synthesized from text
using the text-to-speech engine.
- If the application supports barge-in, the caller can interrupt
the prompt if he or she already knows what to do.
- The application waits for the caller's response for a set period
of time.
- The caller can respond either by speaking or by pressing one or
more keys on a DTMF telephone keypad, depending on the types of responses
expected by the application.
- If the response does not match the criteria defined by the application
(such as the specific word, phrase, or digits), the voice application
can prompt the caller to enter the response again, using the same
or different wording.
- If the waiting period has elapsed and the caller has not responded,
the application can prompt the caller again, using the same or different
wording.
- The application takes whatever action is appropriate to the caller's
response. For example, the application might:
- Update information in a database
- Retrieve information from a database and speak it to the caller
- Store or retrieve a voice message
- Launch another application
- Play a help message
After taking action, the application prompts the caller with
what to do next.
- The caller or the application can terminate the call. For example:
- The caller can terminate the interaction at any moment by hanging
up. Blueworx Voice Response can detect if the caller hangs up and
can then disconnect itself.
- If the application permits it, the caller can use a command to
indicate explicitly that the interaction is over (for example, by
saying “Exit”).
- If the application has finished running, it can play a closing
message and then disconnect.
|

