Blueworx Voice Response has built-in function to communicate with standard TDD devices. The Telecommunications Device for the Deaf (TDD) is a telephony device with a QWERTY keyboard and a small display and, optionally, a printer. Instead of speaking into a mouthpiece, the caller types messages on the keyboard; instead of hearing a voice from the receiver, the caller views the messages on the screen, and can print them for later reading. Usually, both callers use TDDs.
Enabling your Blueworx Voice Response voice applications to communicate with TDDs makes your services and information available to callers who are unable to use an ordinary telephone. Blueworx Voice Response sends TDD characters as if it were another TDD.
With the TDD support, Blueworx Voice Response can exchange data with TDD devices without any additional hardware. Both the US (45.45) and European (50.00) baud rates can be used.
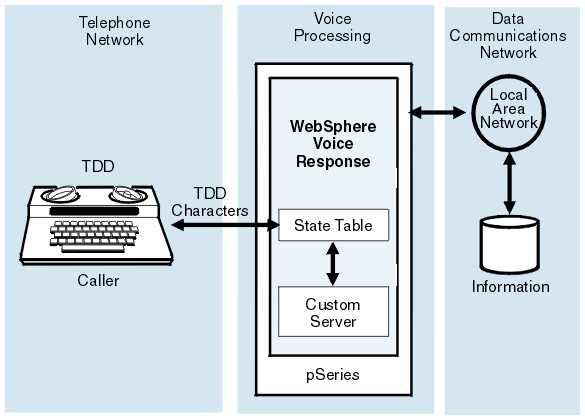
A TDD application works in much the same way as a voice application, with a state table, prompts and TDD-character (rather than voice) segments, together with a custom server that uses specialized subroutines to recognize and generate TDD characters dynamically. Writing a TDD application is similar to writing a DTMF-replacement application that uses discrete-word speech recognition; the application recognizes TDD characters sent by the caller, bases its decisions on them, and replies using TDD characters.
Specially tailored prompts and TDD-character segments are supplied in a form suitable for U.S. English—if you want to support TDD users in other languages, you can define other TDD languages.
Blueworx Voice Response's support is designed to operate with devices meeting the EIA Standard Project PN-1663 TDD Draft, 9 June 1986 specification.