Integrated Services Digital Network
In contrast to Signaling System 7, the ISDN primary rate interface (PRI) is designed as an access protocol, and is therefore also known as primary rate access (PRA).
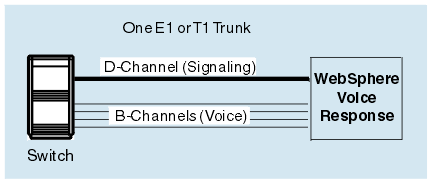
An ISDN trunk is a T1 or E1 trunk with one of the timeslots dedicated to signaling: this is called the D-channel. (The D-channel signaling protocol is based on the ITU-T Q.921 and Q.931 recommendations.) The remaining timeslots are used for voice and are called B-channels (see Figure 2). ISDN trunks are generally used between an external subscriber and a switch within a network. ISDN will eventually displace channel associated signaling (that is, T1 and E1 trunks) as the means by which primary-rate subscribers attach to SS7-controlled networks.
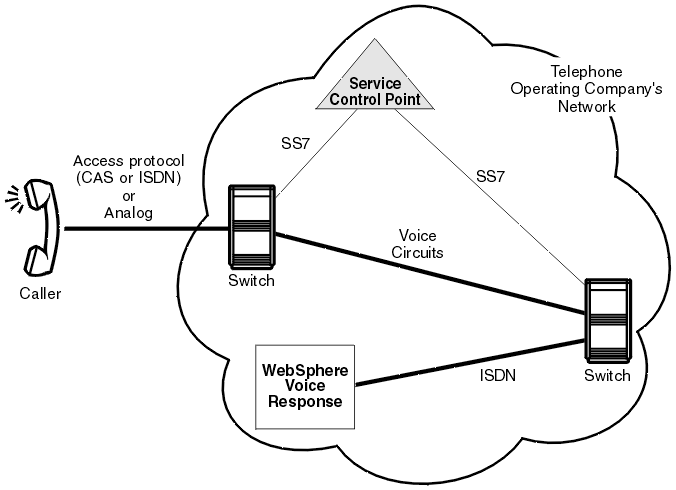
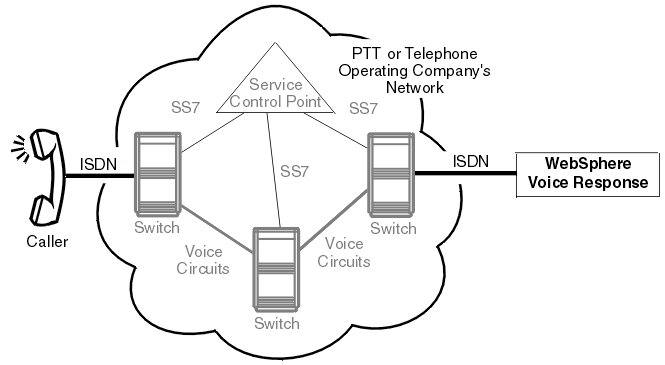
In addition to being used as an access protocol, in the U.S., primary rate ISDN is used to attach intelligent peripherals within an operating company's advanced intelligent network (as shown in Figure 3). Blueworx Voice Response can either function as an intelligent peripheral or provide voice processing function as part of a larger service node.
Advantages of ISDN
The usual justification for ISDN is that a single digital channel can be used for several different types of communication services, for example, voice, X.25, video, and so on. However, for Voice Response Units such as Blueworx Voice Response, ISDN offers a further set of benefits even if the Voice Response Unit is only ever used for voice:
- Reliable call setup and clearing
- Reliable delivery of called and calling number to the Voice Response Unit
ISDN standards supported
The optional ISDN features support:
- Primary rate interface (PRI) vendor-specific implementations
- PRI switching and signaling capabilities
- Calling number identification services for PRI
There is an optional feature of Blueworx Voice Response to interface to the network over an ISDN primary rate interface that conforms to each of the following standards:
- Euro-ISDN
- Lucent 5ESS 5E8
- Lucent 5ESS 5E9 National
- Lucent TR41449/TR41459
- Nortel DMS100 BCS34/36
- Nortel DMS100 National 2 — NA007/008
- Nortel DMS250 — IEC05
- National ISDN2/5ESS 5E12/13
- INS Net Service 1500
For more detailed information about how Blueworx Voice Response supports ISDN protocols, refer to the Blueworx Voice Response for AIX: General Information and Planning information.