This section describes the sequence of events following a channel process failure.
Figure 1. Common channel signaling process: channel process
failure
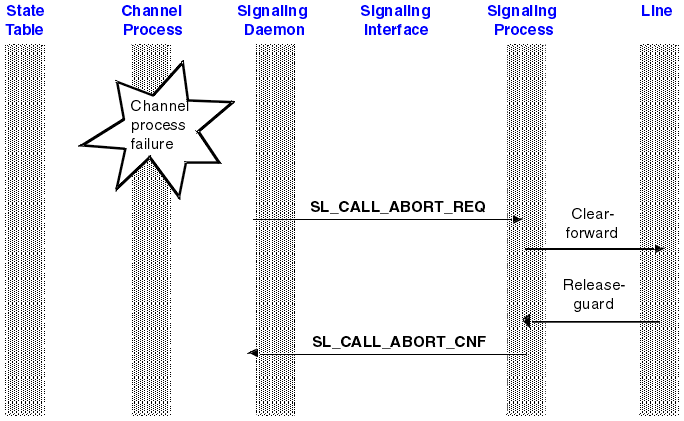

Description of flows
The flows shown in Figure 1 are as follows:
- A failure occurs in the channel process interpreting the application’s state table.
- The failure of the channel process is detected by the signaling daemon, which is a component of Blueworx Voice Response.
- The signaling daemon creates an SL_CALL_ABORT_REQ primitive, and sends it to the signaling process responsible for the call. The SL_CALL_ABORT_REQ primitive is an instruction to the signaling process to clear the call to the network.
- The signaling process is waiting for primitives from the signaling interface using the sl_receive_request() subroutine. The call to sl_receive_request() completes, and the signaling process receives the SL_CALL_ABORT_REQ primitive.
- The signaling process clears the call to the network. The signaling process should clear the call as quickly as possible.
- After the call is cleared, the signaling process creates an SL_CALL_ABORT_CNF primitive, and sends it to the signaling daemon using the sl_send_confirm() subroutine call.
- The signaling daemon is waiting for the reply from the signaling process, by using the sl_receive_confirm() subroutine. If the signaling process does not send back the SL_CALL_ABORT_CNF primitive, or if the ReplyCode in the primitive is not SL_REPLY_SUCCESS, the signaling daemon logs an error to the Blueworx Voice Response system monitor.