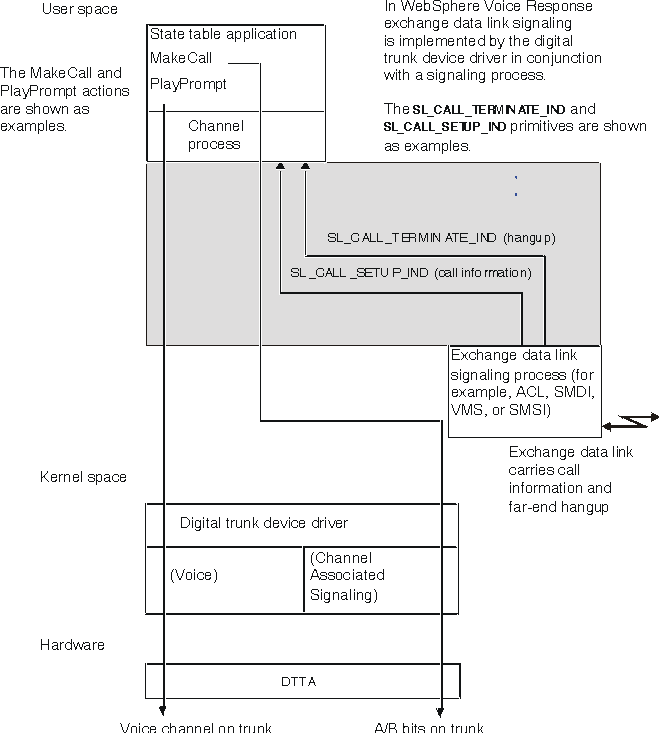
Figure 1 shows the system components involved in processing a voice application when using an exchange data link and channel associated signaling. Telephony actions, such as MakeCall, result in signaling information being sent on the digital trunk. Voice processing actions, such as PlayPrompt, result in audio signals being sent on the voice channel.
In addition, the exchange data link provides additional signaling information, such as call information when the call is received, and hangup notification when the call is terminated by the network. This information is received by the signaling process and sent to the channel process across the signaling interface.
Outgoing call setup
State table MakeCall actions are interpreted by the channel process, and passed to the digital trunk device driver, which performs the channel associated signaling required. When the signaling is complete, the digital trunk device driver returns control to the channel process, which maps the result into an edge which is returned to the state table.
Incoming call setup
Incoming calls are detected by the digital trunk device driver, which notifies the channel process manager. Simultaneously, call information is sent across the exchange data link. The signaling process is responsible for passing this information to Blueworx Voice Response. The call information is available to the channel process manager and channel process from the signaling interface. The channel process manager determines which state table to execute, and a channel process is allocated to run the state table.
Call clearing initiated by Blueworx Voice Response
State table TerminateCall actions are interpreted by the channel process, and passed to the digital trunk device driver, which performs the channel associated signaling required. When the signaling is complete, the digital trunk device driver returns control to the channel process, which maps the result into an edge that is returned to the state table.
Call clearing initiated by the network
Incoming clear notifications can be received over the exchange data link. The signaling process then notifies the Blueworx Voice Response system of the event. In this case it is not necessary for the digital trunk device driver to monitor the voice energy level, or look for constant or cadenced tones on the line, to detect when the caller has hung up. Clear notification over the exchange data link is also much quicker than monitoring voice energy or tones, which means that there is a shorter delay before the channel can be reallocated for a new caller.