An exchange data link is one way of overcoming some of the disadvantages of channel associated signaling protocols, by exploiting the host access control links provided by many switches. An exchange data link is used in conjunction with a channel associated signaling trunk. The call is established and cleared using signaling sent over the trunk. The exchange data link provides supplementary information, such as the dialed number.
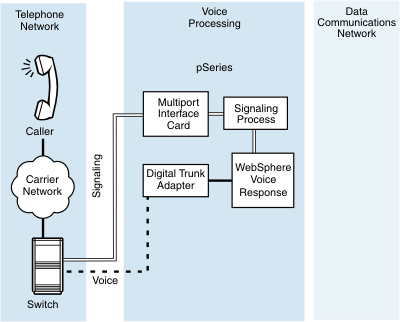
Such a control link passes telephony event information and traffic statistics to a computer and can also allow the computer some control over the switch. This is commonly known as computer-telephony integration (CTI). If your switch supports this, you can use a Blueworx Voice Response exchange data link to provide the signaling functions that are not provided by the channel associated signaling protocol. For example:
- The telephone number that the caller dialed could be sent from the switch to Blueworx Voice Response, to be used to choose the application to answer the call.
- The telephone number from which the call was forwarded could be sent from the switch to Blueworx Voice Response.
- Blueworx Voice Response could send a message waiting indicator to the switch, to signal that the message waiting lamp should be turned on or off (or a stutter tone introduced) on the called party’s telephone. The switch can send a response if it is unable to process the message waiting indicator.
The following types of exchange data link are provided with Blueworx Voice Response and require no additional programming:
- Simplified Message Service Interface (SMSI), for use with the AT&T central office switch
- Simplified Message Desk Interface (SMDI), for use with the Northern Telecom DMS100 central office switch
- Voice Message Service (VMS), for use with the Ericsson MD110 PABX
- Application Connectivity Link (ACL), for use with the Siemens Hicom 300 PABX.
- The CallPath_Sigproc custom server, for use with switches supported by CallPath Server.
If your switch does not use SMSI, SMDI, VMS, or ACL, but has a host access control link, you can write a signaling process to interface with it, to provide functions such as call transfer, message waiting, and call monitoring.